Often times you hear of designer breeders claiming that their mixes are registered with TICA. I would like to clear this up, as I’m sure it’s confusing for your average pet owner to differentiate between the different types of registrations we have. In TICA, we maintain Experimental Records for “breeds” which are not recognized for the purpose of tracking lineage of unrecognized breeds or mixes. This is not the same as a registration, and any cat in the Experimental Record is ineligible for competition in TICA unless it is altered and registered as a household pet. Experimental Breeds do not have to be approved by the board of directors for recording purposes, this is the entry level into trying to establish a new breed and as such there can by any nonsensical combination of mixes in this category. If one were foolish enough, one can mix 30 breeds together, call it Unicorn Poop, and record it in the Experimental Record. Having Experimental Record slips in no way implies that TICA will accept this mix as an established breed, and simply seeing how long these mixes have sat stagnant at that stage without advancement is pretty indicative of that, considering an Experimental breed is only required to maintain themselves there for one year before being eligible to apply for advancement. In the case of Bambino, Elf, Dwelf, Bambob, Sphynxbob, Skinderlop etc, a rule was put in place making advancement or acceptance as a breed impossible;
Registration Rule 33.2.1 Domestic Hybrid Breed – A breed developed from a deliberate cross between two existing domestic breeds, incorporating characteristics of both parental breeds into the new breed. Breeds that have a STRUCTURAL MUTATION as a breed characteristic must not be used as source breeds.
31.6 Structural mutation: Appearance of the skeletal and/or cartilage expression different from the average domestic cat such as, but not limited to, folded ears, shortened legs, shortened or absent tail, etc. The difference in expression may or may not affect the physical abilities of the cat.
Another important rule of interest;
Registration Rule 33.2.4 Mutation Breed – A breed which has been defined by the introduction of new gene(s) NOT PRESENT in an established breed.
The mutations responsible for the phenotype of Mutation Breeds cannot be used in creating new recognized mixes. In essence, the Munchkin breed own their dwarf mutation, the Scottish Fold breed own their cartilage mutation, the American Curl breed own their curl mutation etc.
Registration Rule 39.4 Structural mutations are “owned” by the first breed establishing championship status that displays that structural mutation (such as folded ears: Scottish Fold; short legs: Munchkin; curled ears: American Curls, etc.) New breeds may only use this structural mutation with permission (a majority vote of the breed section) of the breed/breed group owning it.
I hope this clarifies the position of TICA and the cat fancy regarding the acceptance, recognition and discouragement of these designer mixes.
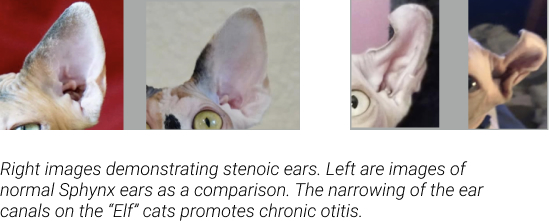
The “Elf”
This is an American Curl mixed with Sphynx. The American Curl is a healthy breed of cat with a dominant mutation responsible for the curled ear. Similarly to the Sphynx, this breed derives from a natural mutation in Domestic Shorthairs, and as such have a prevalence for HCM similar to their DSH foundation (HCM in DSH is estimated to be anywhere from 10-17%). Because of the ear mutation and the copious ear wax seen in the Sphynx, they have an increased incidence of Otitis, and often times deal with stenoic ear canals from vertical crimps in the ear (something AC breeders specifically try to avoid in their programs).
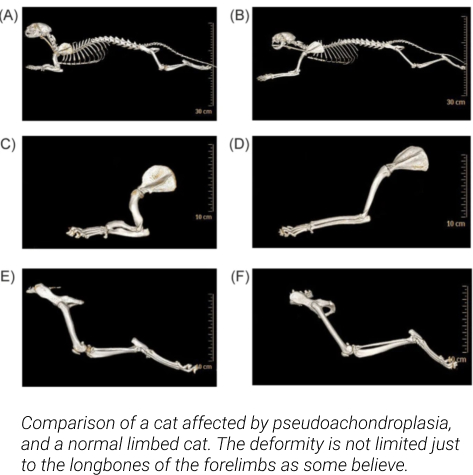
The “Bambino”
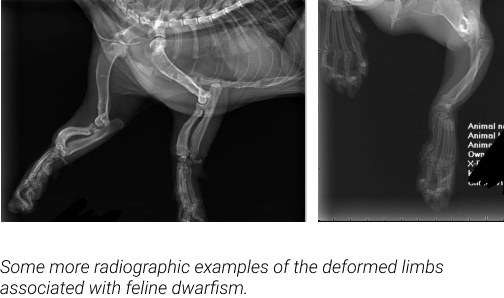
This is a Munchkin mixed with Sphynx. This results in a dwarfed hairless cat, unfortunately with a long list of potential medical complications. The mutation responsible for the Munchkin phenotype is a deformity called Pseudoachondroplasia (a deletion of 3033 base pairs in the UGDH gene) and it is lethal in its homozygous state (fetuses inheriting two copies of the gene die in utero and are reabsorbed). The deformity has an increased risk of Spinal Lordosis, Pectus Excavatum, Flat Chested Syndrome, Hip Dysplasia, Elbow Dysplasia and severe joint malformation, arthritis as a result of uneven weight distribution on the carpus from the curvature of the ulna and radius, stress fractures, and mandible injuries from jumping off high surfaces with insufficient reach in the forelimbs to stop the trajectory of the face when landing. Again, this is a naturally occurring deformity/mutation in domestic shorthairs and also accompanies the risk of HCM. This risk is compounded when introducing the Sphynx into any potential mix.
The “Dwelf”
This is an American Curl mixed with Sphynx and Munchkin. This not only combines the risk of the two afore mentioned mixes, but also introduces a chaos factor with no idea how these mutations will react and interact with one another. Unless one is a geneticist with the well being of the animals in mind, one should not be playing with such significant genetic mutations willy nilly.
The “Sphynxbob”
This is an American Bobtail mixed with Sphynx. This results in a tailless, hairless cat. American Bobtails are a natural mutation from domestic shorthairs and have an incidence of HCM as a result, along with a higher rate of spine associated birth defects, hip dysplasia, prolapsed rectums, sacrocaudal dysgenesis and paralysis in severe cases in comparison with tailed breeds. The mutation is variable and can result in a short bobtail or in a complete lack of tail altogether which drastically increases health complications.
The “Bambob” incorporates yet another structural mutation on top of the “Sphynxbob”, with the addition of dwarfism.
Please note, the images of these defects are too graphic to share publicly, but can be made available upon private request.
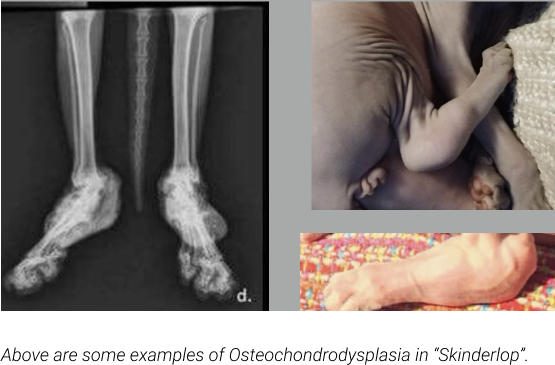
The “Skinderlop”
This is a Scottish Fold mixed with Sphynx. This results in a hairless cat with ears folded forward. The Scottish Fold mutation is dominant and is directly linked with Osteochondrodysplasia, a progressive musculoskeletal disease that results in debilitating skeletal growths, deformities and incredible pain. There have been several studies that conclude that all folded eared cats are affected by Osteochondrodysplasia to one severity or another (Malik et all, 2001). Scottish Folds also have a high incidence of HCM, and recently were accepted for a breed specific HCM study to try to locate a gene marker for HCM in the breed. Scottish Fold breeders are working tremendously hard to improve the health of their breed and the bastardization of their breed in these unsanctioned mixes is not only detrimental to the unfortunate Skinderlop being produced, but also to the SF gene pool.
-Shauntay Burris